EDAIC or PLAB for IMG Anaesthetists
02 Oct, 202314 Minutes
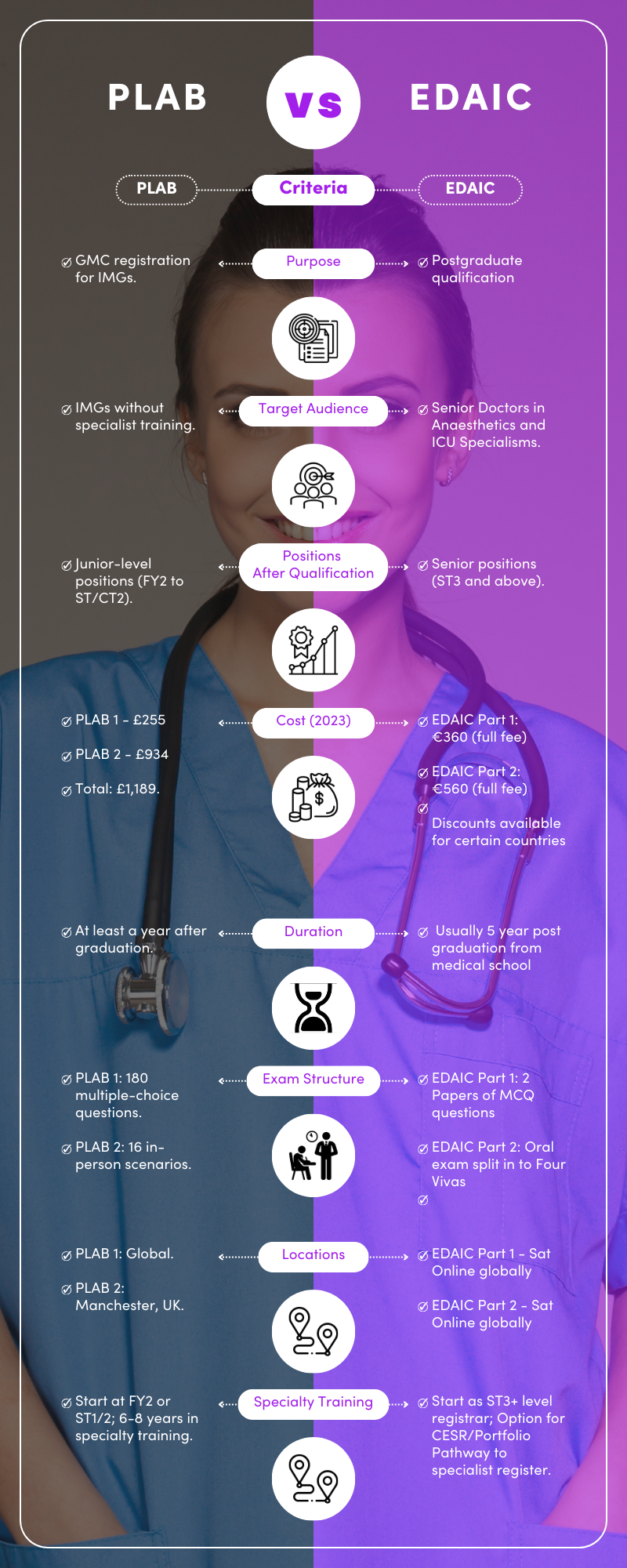
EDAIC is a postgraduate qualification aimed at senior Anaesthetics and ICU doctors whereas PLAB is a general entry examination that grants junior doctors access to the GMC register. In fact, both options allow a good entry route to the GMC however they’ll lead to different starting points in your NHS career. You’ll also need to weigh up the costs, time to complete, exam structures and test centre locations. This article define, compares and contrasts EDAIC and PLAB so that you can make an informed decision on which is best for you.
What are PLAB and EDAIC?
First, let’s start with definitions. PLAB – standing for the Professional Linguistic and Assessment Board – is a two-part examination that provides an entryway for GMC registration. It assesses you to the same level as an NHS FY2 level doctor and doesn’t hold much weight aside from that; you’ll need more experience or a postgraduate qualification if you want to attain a higher position.
On the other hand, EDAIC is a multilingual examination that covers anaesthesiology. It’s a qualification intended to be held at the end of anaesthesiology/intensive care training, and its completion shows high levels of anaesthesiology knowledge and the ability to work as an anaesthetist at a senior level. Like PLAB, it can also be used for GMC registration but also proves that you have a greater level of experience.
Who Are PLAB and EDAIC aimed at?
PLAB is for international medical graduates who want to start work in the UK as soon as possible after graduating from medical school. They will usually have a year or so of experience after medical school and be willing to go through the UK’s training system from ST1 level to pursue a specialty down the road at a more appropriate time in their career.
EDAIC is for doctors who want to prove their expertise in anaesthetics. IMGs taking EDAIC will have pursued anaesthesiology or ICU training overseas and want to use that training to start their NHS career in a higher position. By the time they move to the UK, they are already experts in anaesthesiology and are able to begin their career at a senior level, whether as a registrar, specialist, specialty doctor, or Consultant anaesthesiologist.
What Jobs Can You Get after PLAB vs EDAIC?

PLAB
Once you have completed PLAB and used it for GMC registration, you’ll be able to start applying for NHS roles from the level FY2 (which is the second year of foundation training), earning a salary between £32,398 and £37,303 per year. However, PLAB can lead to positions at the same level as CT/ST 1+2, depending on your experience. It is possible to apply for ST3+ level posts so PLAB doesn’t exactly stop you from pursuing a senior position. However, it should be noted that PLAB doesn’t look as favourable on a senior doctor’s CV, especially if you want to go straight into specialty training where a more advanced qualification is essential.
EDAIC
Once you have obtained EDAIC, you can apply for anaesthetics positions within the NHS, either as a registrar, specialist, specialty doctor, or even as a Consultant where you might do CESR/ Portfolio Pathway to get on the specialist register. These anaesthesiology positions will most likely be at ST3+ level, and you’ll be able to earn a high salary while pursuing the specialty you want – anaesthetics. As a specialty doctor, you can earn between £52,530 to £82,400; as a specialist grade doctor, you’ll earn between £83,945-£92,275; and as a Consultant, you’ll earn between £93,666-£126,281. These are basic salaries so if you work more hours or partake in an out of hours rota then you can expect to earn even more.
To get an idea of current job options you can start a job search or register with BDI Resourcing.
Which is more expensive – PLAB or EDAIC?
Both the PLAB and EDAIC examinations come with their own fees. Naturally, you’ll want to know exactly how much these exams will cost you – especially when you’ll already be planning a budget for relocating to the UK! The difference in cost between these exams might even impact which one you choose (although there are other considerations to keep in mind other than upfront costs).
PLAB
The PLAB exams include PLAB 1 and PLAB 2. PLAB 1 costs £255, while PLAB 2 costs £934, so that’s a total of £1,189. These prices are from April 2023 – you may notice an increase if you’re booking after that time.
EDAIC
The cost of EDAIC differs depending on where you take the tests from – there’s a full fee, a fee for European middle-income countries, and a fee for mandatory or recognised countries (such as Hungary and Romania).
Part 1: €360 (full fee), €270 (middle-income countries), €180 (mandatory or recognised countries)
Part 2: €560 (full fee), €420 (middle-income countries), €280 (mandatory countries)
As you can see, both are expensive exams to sit so you’ll want to be sure that you plan to use them and that you’re choosing the right option for you.

PLAB Vs. EDAIC: Which Takes Longer?
PLAB and EDAIC are different in several ways, including in how long they take to complete.
PLAB is a two-part exam that you can take as soon as you get your PMQ. Its ease of access means you can complete PLAB pretty quickly. However, it’s recommended that you spend at least three months revising before part 1 and part 2 of PLAB. Keep in mind that you’ll also need at least a year of internship experience before you’ll be able to get GMC registered. So, expect PLAB to take at least a year after graduating. For many, it takes a couple of years.
EDAIC takes longer as it’s a qualification granted to anaesthesiologists who have a lot of experience in their branch of medicine. While EDAIC part one is open to those who have a medical degree, you can only take part two if you are towards the end of your anaesthetic training program. Generally, you should try to have at least three years of anaesthetics training to pass part one and five years for part two.
With PLAB potentially taking as little as a year and EDAIC taking five years, it’s clear to see which one is quicker! However, that difference makes a lot of sense when you consider how much weight EDAIC holds as a qualification – it’s a very highly regarded one that shows your competence as an independent anaesthesiologist. With it, you can get higher-level jobs and earn a lucrative salary as an anaesthesiologist in the NHS.
Pursuing Specialty Training with EDAIC Vs. PLAB
Are you interested in pursuing specialty training or getting on the specialist register? Naturally, most IMGs are, as the specialist register leads to senior posts with lucrative salaries and a good amount of responsibility. Both PLAB and EDAIC can lead to senior roles – the difference is how long it takes to get there. With PLAB, specialty training positions may take a little longer to achieve.
Specialty Training with PLAB
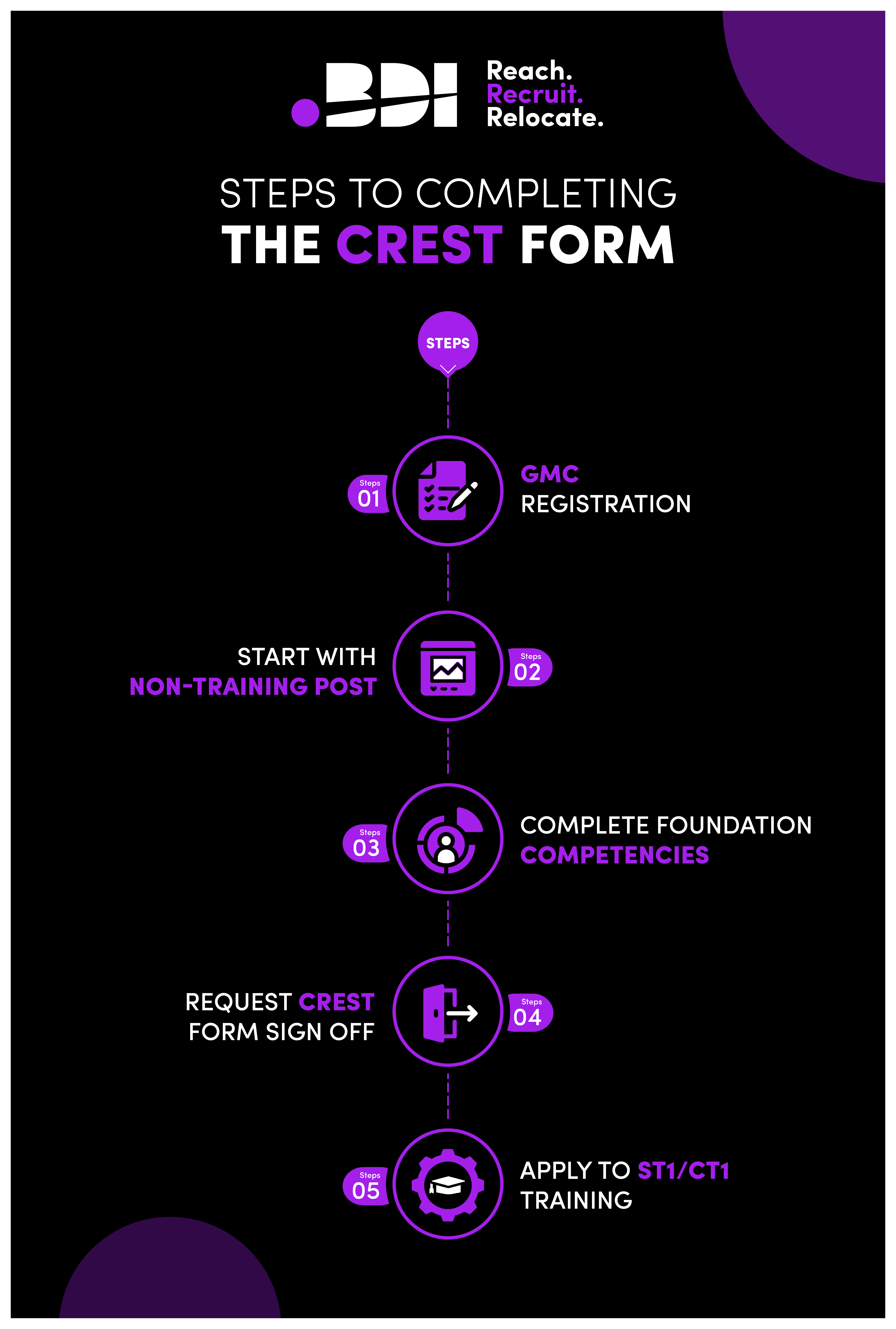
Typically, after getting GMC registered with PLAB, you can start an NHS job in a junior-level service position. This time is best spent learning the ropes and figuring out what you might want to do in the future. Learning a new healthcare system will take time, after all, and you may want to focus on this aspect of your transition rather than immediately working on moving up the ladder. After a year or so of this, you can complete you CREST form and choose to apply for specialty training positions in a specialty of your choice. Starting at ST/CT 1+2 and then moving onto ST3+, you’ll be able to complete your entire specialty training in the UK, which will grant you access to the specialist register via CCT at the end of it. It’s a long process, but it makes sense for IMGs who have recently graduated and want to start work as a doctor in the UK as soon as possible.
To learn more about getting your CREST form complete you can read our guide on Understanding the CREST for for IMGs or follow these steps:
Speciality Training with EDAIC
With EDAIC, you can enter senior roles from ST3+. This is because EDAIC proves you have the knowledge needed to work in anaesthesiology and intensive care at an independent level. Once you join a service role, you can with apply to and work through the UK training system from ST3 level, gaining experience as you go and eventually getting on the specialist register through CCT or CESR-CP. Then, you can work as a Consultant.
You have another option: joining the specialist register straight away. You can do this through CESR (Certificate of Eligibility for Specialist Registration)/ Portfolio Pathway, which is a route for IMGs to specialist registration that doesn’t require UK training. By using EDAIC for your CESR/ Portfolio Pathway application (which involves submitting a lot of evidence to prove your capabilities), you may be approved, which will grant you access to the specialist register. Both routes will lead you to specialist registration so you’ll need to establish how much experience you can evidence to the GMC and what gaps you might need to fill in. CESR / Portfolio Pathway is often considered a difficult route of entry for overseas doctors unless they are already working in a very senior capacity.
EDAIC Exam Structure

What about exam structure? As you may have probably guessed, the EDAIC exams are extremely rigorous – you will only pass them if you have a good amount of knowledge of anaesthesiology and plenty of experience. It comes in two parts, and here’s what to expect in each one:
EDAIC Part 1
EDAIC part one runs twice yearly. The exam is split into two papers: paper A and paper B. There are sixty multiple-choice questions on each paper, with a potential five answers to choose from. You get two hours per paper if you complete the exam on physical paper and ninety minutes if you complete it on a computer.
Paper A covers basic sciences regarding anaesthesiology, including physiology and anatomy, whereas paper B covers core clinical topics, such as intensive care medicine.
EDAIC Part 2
Like part 1, EDAIC part 2 runs twice per year. That’s where the similarities end, as EDAIC Part 2 is an oral exam. This means you’ll need excellent spoken communication skills to pass it.
Part 2 is split into four vivas, and each viva involves speaking with two examiners for twenty-five minutes. The topic of conversation revolves around a given clinical scenario; the examiners will ask you questions and you’ll provide answers, showing the examiners how you would handle the clinical situation. Each viva covers different areas of anaesthetics, including applied basic sciences and clinical critical care.
As a multilingual exam, you’ll be able to take the EDAIC exams in any of the following languages:
- English
- French
- German
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Spanish
- Scandinavian
- Turkish

PLAB Exam Structure
So, what can you expect on the day when sitting PLAB? PLAB has two parts: PLAB parts one and two. Passing both is essential for completion. Here is the exam format for each:
PLAB Part 1
PLAB part one is a written multiple-choice exam with 180 questions in total. The questions give you a clinical scenario and ask you to choose the best of the five answers provided, and you get three hours total to complete it. You can take PLAB Part 1 in multiple locations around the world, including in the UK and in international test centres.
PLAB Part 2
PLAB 2 is a little different – it’s a practical exam that tests your in-person clinical abilities. It’s a day-long test that includes sixteen stations, where you’ll find two examiners and a mock clinical situation to assess. You get eight minutes at each station and two stations that offer a resting break. PLAB part two only takes place in the UK (specifically, Manchester), so you’ll have to travel there to complete PLAB.
Exam Locations: EDAIC
Part 1 has a large number of countries where it can be taken.
EDAIC Part 1:
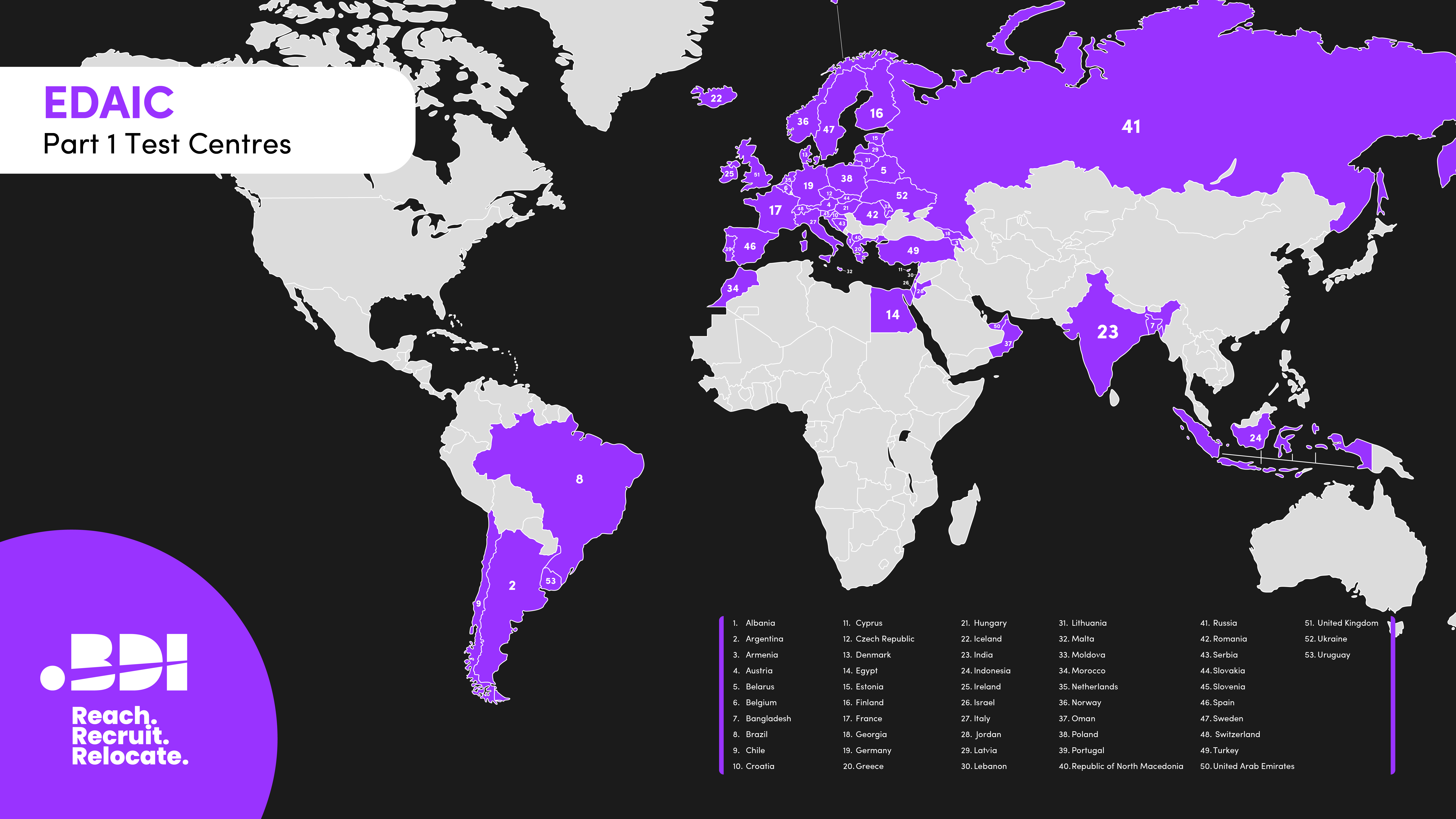
- Albania
- Argentina
- Armenia
- Austria
- Belarus
- Belgium
- Bangladesh
- Brazil
- Chile
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Czech Republic
- Denmark
- Egypt
- Estonia
- Finland
- France
- Georgia
- Germany
- Greece
- Hungary
- Iceland
- India
- Indonesia
- Ireland
- Israel
- Italy
- Jordan
- Latvia
- Lebanon
- Lithuania
- Malta
- Moldova
- Morocco
- Netherlands
- Norway
- Oman
- Poland
- Portugal
- Republic of North Macedonia
- Russia
- Romania
- Serbia
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Sweden
- Switzerland
- Turkey
- United Aad Emirates
- United Kingdon
- Ukraine
- Uruguay
EDAIC Part 2
Most EDAIC examinations took place online in 2023, and this may continue going forward. However, there were some physical test locations, including:
- Madrid
- Uppsala
- Malta
- Istanbul
- Warsaw
- Erlangen
Exam Locations: PLAB
Part One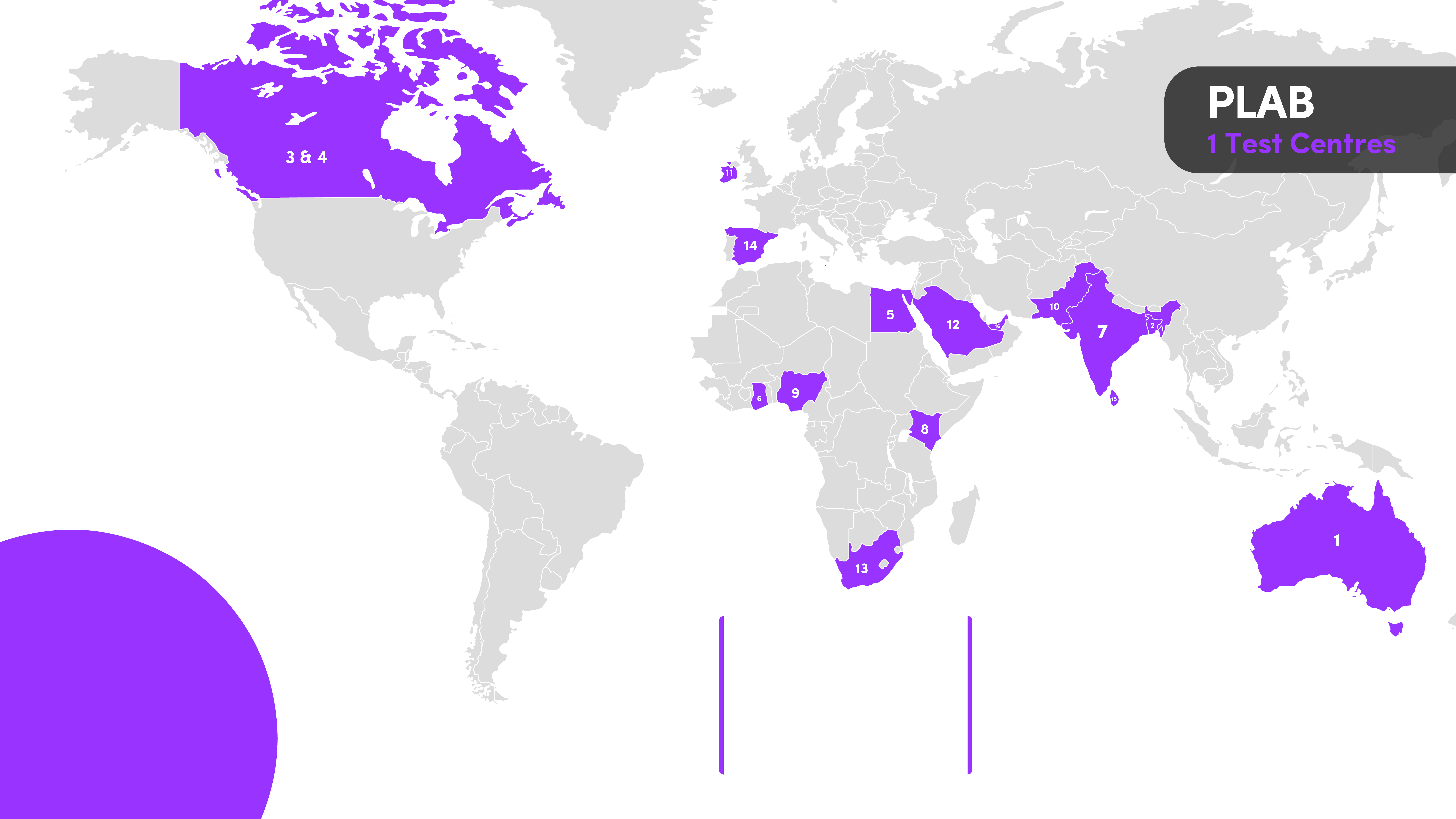
UK Locations:
- Belfast
- Birmingham
- Cardiff
- Edinburgh
- London
- Manchester
- Newcastle
- Oxford
- Sheffield
Overseas Locations:
- Sydney, Australia
- Dhaka, Bangladesh
- Toronto, Canada
- Alexandria, Egypt
- Cairo, Egypt
- Accra, Ghana
- Bangalore, India
- Chennai, India
- Hyderabad, India
- Kolkata, India
- Mumbai, India
- New Delhi, India
- Nairobi, Kenya
- Abuja, Nigeria
- Enugu, Nigeria
- Lagos, Nigeria
- Islamabad, Pakistan
- Karachi, Pakistan
- Dublin, Republic of Ireland
- Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
- Johannesburg, South Africa
- Madrid, Spain
- Colombo, Sri Lanka
- Dubai, UAE
Part Two
Unlike PLAB Part One, PLAB Part Two does not have multiple test centres where you can sit the exam. Instead, you have to travel to one city in the UK (Manchester in the North of England) as all PLAB 2 exams take place here. There are no exceptions to this – everyone will need to book their visas and planes and travel.
Getting GMC Registered with PLAB or EDAIC
We have gone over the vast array of differences between PLAB and EDAIC in this article. However, one thing still rings true: both of these qualifications grant access to GMC registration. In that aspect, they hold the exact same weight! So, if your goal is simply to get GMC registered and start work as a doctor, either will work.
There are some other things you’ll need to provide to the General Medical Council to get on the register, and that includes:
- Passport
- Proof of Internship
- Evidence of Last Five Years of Practice
- Evidence of Knowledge of English
- Certificate of Good Standing
- Fitness to Practice
- Primary Medical Qualification
With the above documents – as well as either PLAB or EDAIC – you can get on the GMC register and start practising as a doctor in the UK. PLAB and EDAIC only affect the types of jobs you can apply for – as well as the chances of getting those positions.
In Summary
Getting GMC registered is essential for any doctor – UK-based or otherwise – wanting to practise medicine in the UK. It’s how you go about it where you have some flexibility. If you want to get GMC registered as soon as possible and you have no specialty experience, PLAB makes sense. However, if you’re interested in working in anaesthesiology or intensive care and/or have experience in those specialties in your home country, you could instead pursue EDAIC. When choosing between the two, keep these key points in mind:
- EDAIC is a well-regarded postgraduate qualification.
- PLAB are exams specifically for IMGs for GMC registration.
- Completing EDAIC makes PLAB obsolete
- EDAIC leads to better-paying, senior positions within the NHS.
Choosing the right entryway into the UK is important, as it shapes your career from the get-go. Both options are fine for the right person – it’s all about your individual goals and current experience.
BDI Resourcing - your partner for EDAIC or PLAB
As the most trusted and best rated experts in international and domestic recruitment for the NHS, BDI Resourcing are ready to help you on your next career step. If you would like to hear more about your options for new roles across the UK or you'd just like some advice, support and guidance on the process of GMC Registration, CV preparation or interview questions then get in touch with our expert team.



