PLAB Vs MRCPCH for Paediatrics IMGs
14 Sept, 202315 Minutes
If you’re interested in relocating to the UK to work as a doctor in paediatrics, then you have two choices. You can either sit PLAB or MRCPCH. Both will give you entry to the GMC register however they are different in many ways. If you’re wondering which is the best for you then we’re here to help you.
Firstly, GMC registration is an absolute must for any international medical graduate wanting to work in the UK. Even UK-based doctors need to be on the GMC register, as it shows they can practise medicine safely. Of course, getting on the GMC register is a little different for IMGs than it is for UK citizens; it requires certain qualifications to demonstrate your abilities. One popular route is PLAB, an assessment made specifically for IMGs to prove they are at the same level as UK FY2 doctors. For paediatricians with specialist training behind them, you have the option of the MRCPCH postgraduate qualification to help you start a UK career at a higher level.
Who Are PLAB and MRCPCH For?
First, we need a definition. PLAB stands for the Professional Linguistic and Assessment Board and is an assessment aimed at overseas doctors who want to work in the UK. The exam comes in two parts and is there to ensure all international medical graduates are at the same place as UK FY2 level doctors.
On the other hand, MRCPCH stands for Member of the Royal College of Paediatrics and Child Health. It’s a Royal College postgraduate qualification that tests the candidate’s knowledge and capabilities in that specialty and has three theory exams and one clinical exam. Upon completion, you become a member of the RCPCH and can use this qualification to enter senior-level paediatric positions.
Even with a definition, you might still be in two minds about which one you should do. It’s a big decision, as the choice seriously impacts your career outlook!
You should take PLAB if...
You have achieved your primary medical qualification, and you are either in or about to start an internship/training overseas. You don’t have any specialist training – instead, you want to begin your NHS career as soon as possible. All in all, you’re looking to become a paediatrician by working your way through the UK’s training system.
You should take MRCPCH if...
You are a paediatric trainee doctor or specialist from overseas and want to carry on your career in the UK. You may have even completed your paediatric training in your home country and want to prove your skills and competencies as a paediatric doctor. In general, you consider yourself a specialist in Paediatrics and would like a more senior role in the NHS.
Keep in mind that while PLAB and MRCPCH are different, they both act similarly when it comes to GMC registration. Also, be aware that doing MRCPCH means you won’t need to do PLAB.
The Jobs PLAB and MRCPCH Lead To
While PLAB and MRCPCH both lead to GMC registration – which is a major goal for IMGs wanting to work in the UK – that doesn’t mean they are exactly the same.
PLAB is basically an entryway into working as a UK doctor. It doesn’t actually help you in terms of climbing the ladder; instead, it allows you to join the NHS at a junior level, from FY2 to ST2 (depending on your experience). Strictly speaking it won’t stop you applying for more senior roles however you might be limited since many paediatrics departments won’t be able to support registrar, specialist or Consultant level posts for IMGs without them completing MRCPCH.
On the other hand, the completion of MRCPCH does help you climb the NHS ladder – with this postgraduate qualification, you can join a senior registrar level service job or apply to a higher specialty training program in paediatrics. In some cases, if you have the right amount of paediatric training from your home country, you can even use MRCPCH to join the specialist register via the CESR programme. This will allow you to work as a paediatric Consultant in the UK. However, that’s a hard journey and can be difficult even for those who are experts in the specialty, as you’ll be working for an entirely new healthcare system.
PLAB Vs MRCPCH: Cost
PLAB Costs
You will pay a separate fee for parts one and two. As of April 2023, PLAB part one costs £255, while PLAB part two costs £934. In total, that means you’ll pay £1,189 to complete PLAB. However, be aware that the Professional Linguistic and Assessments Board often puts these costs up each year, so you may have to pay more if you book your exams after 2023.
The cost of MRCPCH is a little more complicated, as costs can vary depending on where you are taking it from.
MRCPCH Theory Exam Costs:
- FOP: £350 for UK and Republic of Ireland, £435 for international locations.
- TAS: £350 for UK and Republic of Ireland, £435 for international locations.
- AKP: £595 for UK and Republic of Ireland, £835 for international locations.
- FOP and TAS (both papers): £595 for UK and Republic of Ireland, £725 for international locations.
(An explanation of the exam names is below under ‘Exam Structure’)
MRCPCH Clinical Exam Costs:
- £833 for UK
- £1230 for Egypt
- £1555 for India and Singapore
- £1605 for KSA, Oman, and UAE
- £1365 for Malaysia and Pakistan
- £1155 for Myanmar and Nepal
- £1300 for Sudan
As you have likely figured out, the PLAB exams are a fair bit cheaper than the MRCPCH exams. While these upfront costs might sway you, don’t forget to consider the amount of money you’ll earn as a UK doctor. By taking PLAB, you’ll earn a junior doctor’s wage, whereas MRCPCH will grant you access to senior-level roles, which pay a lot more. For perspective, doctors in foundation training earn between £32,298-£37,303 per year, speciality doctors earn between £52,530-£82,400 per year, and Consultants earn a basic salary of between £93,666 and £126,281 per year. The higher salaries can easily make up the difference between the exam prices, so you should go with the route that is best for your career goals.
PLAB Vs. MRCPCH: Length of Time
In terms of how long it will take to clear PLAB vs. MRCPCH, there is one that won’t take you nearly as long: PLAB. You can apply for and take PLAB as soon as you have your PMQ, and you only need one year of training to get GMC registered. We recommend between three and nine months of preparation before each PLAB examination. So, realistically, you can get GMC registered with PLAB with just a year of experience after graduation.
MRCPCH takes a little longer to pass (which makes sense, being a more specialised qualification). You’ll need two and a half years of clinical training in paediatrics to take the clinical exam. On top of that, you’ll need to have passed all of the theory exams. For the best chance of passing each exam, we recommend a minimum of three months of revision.
While MRCPCH takes longer, it should be noted that you’ll get into higher specialty training much quicker with MRCPCH than if you were to take PLAB. Which you choose entirely depends on your career goals and current experience. If you already have paediatric training from your home country, taking the MRCPCH may make a lot more sense – in this case, PLAB wouldn’t showcase what you already know!
Exam Structure: PLAB
If you want to pass PLAB, learning the exam structure is crucial to know what to expect on the day.
PLAB Part One
Part one is a written exam. It has a total of 180 questions, all of which are multiple choice with a single best answer (out of five). You get three hours in total to complete it, so it’s best to pace yourself well, answering the most obvious questions at the beginning.
PLAB Part Two
Part two is a practical exam. It’s taken in Manchester, UK, and consists of eighteen stations that showcase a clinical scenario that lasts eight minutes. You will need to act as a physician in each of the stations while one examiner asks questions and another assesses you. The exam lasts a day, and you will receive two rest stations in the middle of the clinical stations.
Passing both parts one and two is essential for attaining PLAB. You’ll need to pass part one first, as that’s a prerequisite for applying for part two. Other than that, you only really need your PMQ alongside IELTS or OET for these exams!
Exam Structure: MRCPCH
MRCPCH examinations come in four parts: three theory exams and one clinical exam. You can take the three theory exams in any order at any time, whereas you need to have passed all three theory exams before taking the MRCPCH clinical examination.
Theory Examinations
The three theory examinations include Foundation of Practice (FOP), Theory and Science (TAS), and Applied Knowledge in Practice (AKP). You can take all of these exams on a computer from anywhere in the world. However, you can also take them in test centres, which take place both in the UK and in some areas internationally. You get a total of two hours and thirty minutes per examination.
In terms of questions, these theory exams use a mixture of question types, but the most common you will come across is Single-Best-Answer. Other questions may be best of five, data interpretation, case histories, EMQs, and image-based questions. It’s important to prepare for all kinds.
MRCPCH Clinical Exam
To sit the MRCPCH clinical exam, you need to have passed the three theory examinations. You will also need two sponsors who can assure the RCPCH that you have completed the necessary amount of training required to take the exam.
The MRCPCH clinical exam is a practical examination that often takes place in a hospital. There are twelve clinical situations you need to complete in total, each with examiners and actors. You’ll demonstrate your clinical abilities at each station, including your clinical judgment, communication skills, and knowledge of paediatrics/child health.
PLAB Examination Locations
PLAB Part 1
UK Locations:
- Belfast
- Birmingham
- Cardiff
- Edinburgh
- London
- Manchester
- Newcastle
- Oxford
- Sheffield
Overseas Locations:
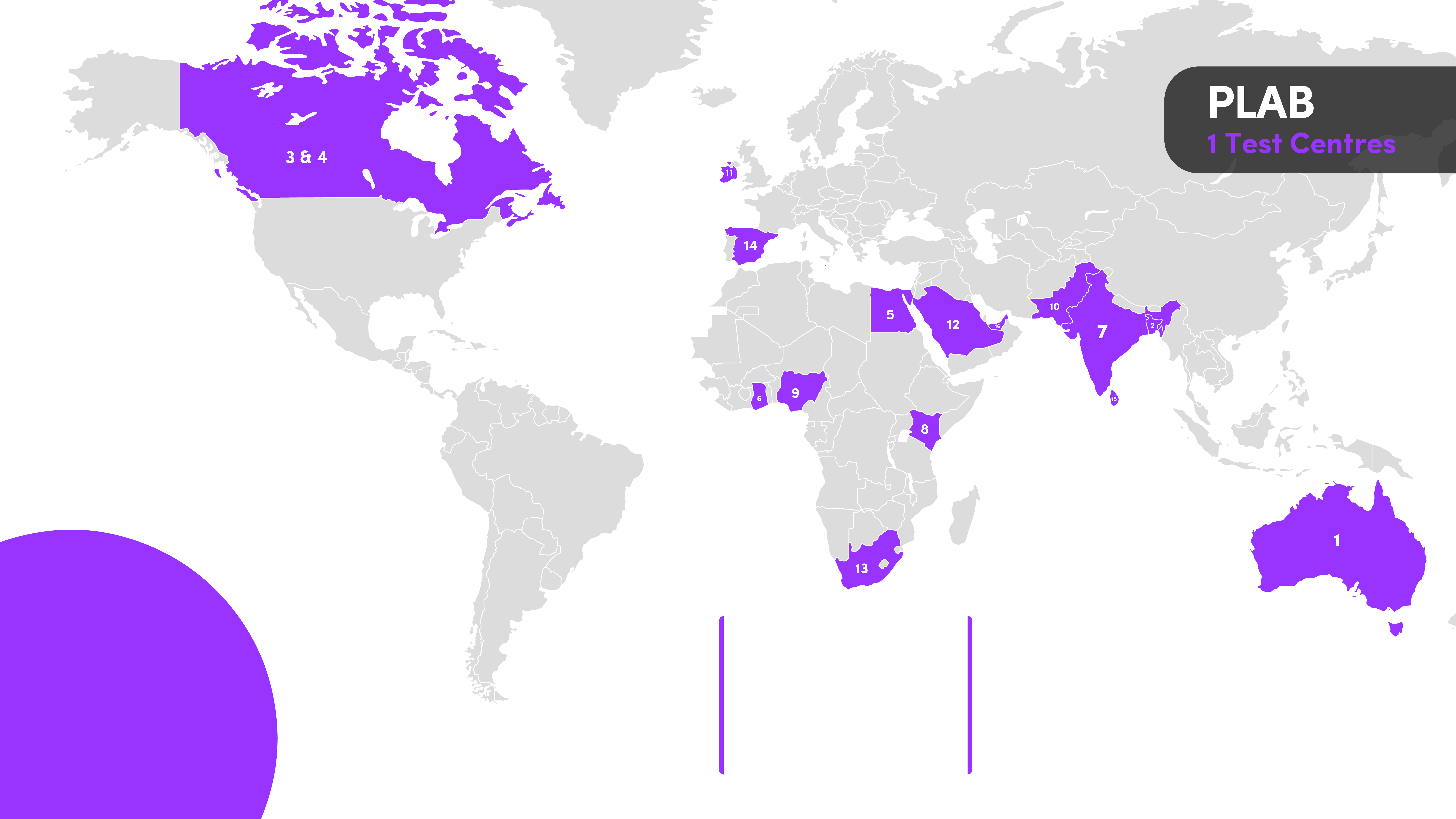
- Sydney, Australia
- Dhaka, Bangladesh
- Toronto, Canada
- Alexandria, Egypt
- Cairo, Egypt
- Accra, Ghana
- Bangalore, India
- Chennai, India
- Hyderabad, India
- Kolkata, India
- Mumbai, India
- New Delhi, India
- Nairobi, Kenya
- Abuja, Nigeria
- Enugu, Nigeria
- Lagos, Nigeria
- Islamabad, Pakistan
- Karachi, Pakistan
- Dublin, Republic of Ireland
- Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
- Johannesburg, South Africa
- Madrid, Spain
- Colombo, Sri Lanka
- Dubai, UAE
PLAB Part 2
PLAB part 2 only takes place in the UK - specifically in Manchester, UK. As such, you will need to travel to the UK no to complete PLAB no matter where you are in the world.
MRCPCH Examination Locations
Theory Examinations
You can take all theory examinations on a computer from anywhere in the world. However, there are specific test centres in the following locations where you can also take them:
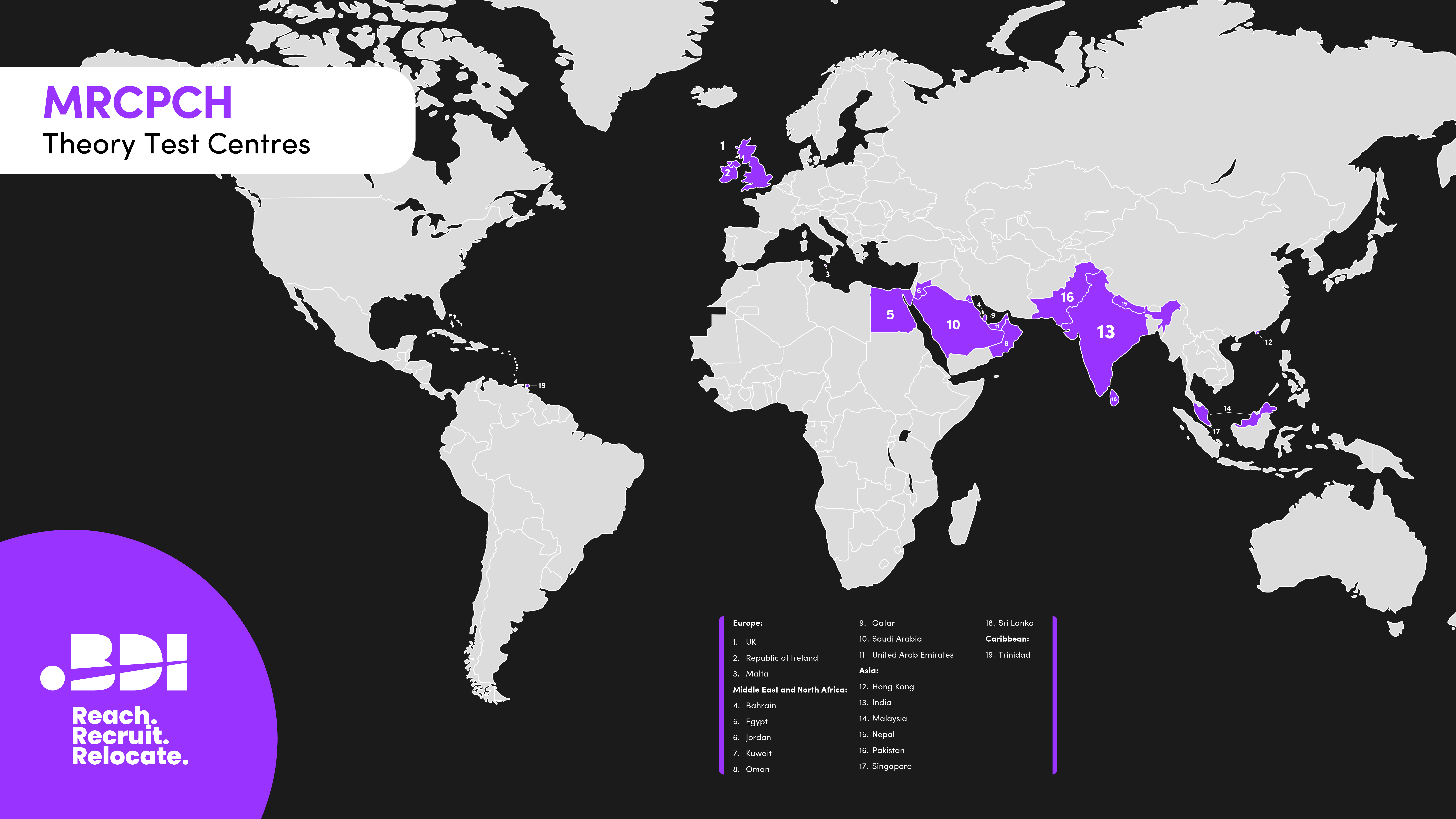
- UK
- Bahrain
- Dubai
- Egypt
- Jeddah
- Kuwait
- Oman
- Riyadh
- Sharjah
- Trinidad
- Chennai
- Hyderabad
- Islamabad
- Lahore
- Kolkata
- Malaysia
- Mumbai
- New Delhi
- Rawalpindi
Clinical Examinations
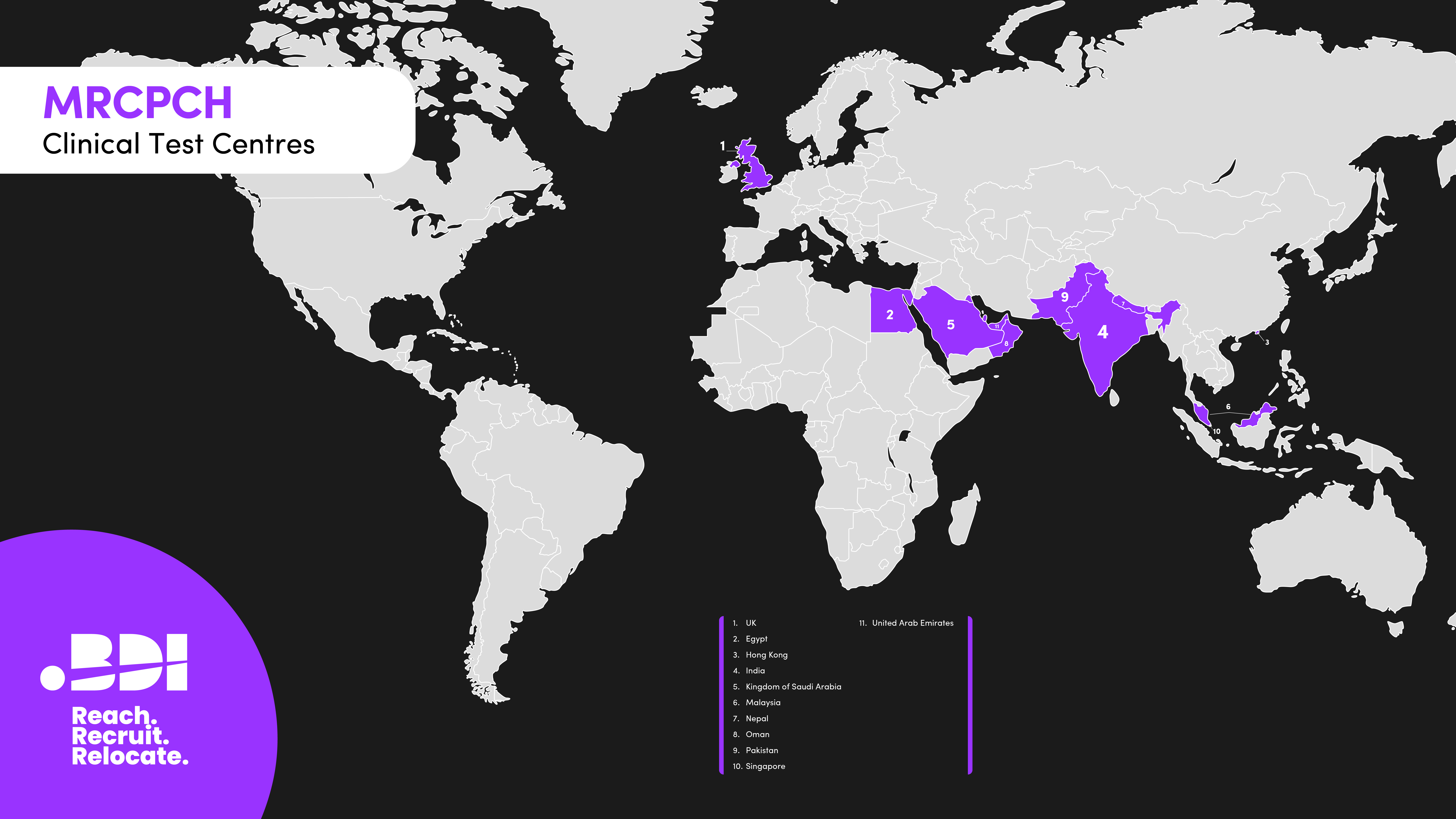
- UK
- Egypt
- Hong Kong
- India
- Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
- Malaysia
- Nepal
- Oman
- Pakistan
- Singapore
- United Arab Emirates
PLAB Vs. MRCPCH: Specialty Training
Do you intend to get on the specialist register? It’s a goal of many UK doctors and IMGs alike. If that’s your goal, it’s a good idea to know where you stand if you have PLAB vs. MRCPCH.
Getting on the specialist register with PLAB is a long journey. PLAB basically tells the GMC that you are at the same level as FY2 UK doctors, so you may have to complete FY2, ST/CT 1+2 before starting your specialty training. If you use PLAB to start at FY2, you can expect to spend three years as a junior doctor before joining higher specialist training, which will involve another six years of training. After that, you can join the specialist register.
MRCPCH allows you access to specialty training roles straight away, starting at ST3 and above. With MRCPCH, you can even get CESR/Portfolio Pathway to join the specialist register without having to follow the CCT pathway at all! It takes a lot of work – and hundreds of pages of evidence – but for international doctors with a wealth of paediatric experience and expertise, it’s a viable route.
There’s also the option of CESR-CP/Portfolio Pathway. This involves using a combination of training from your home country and UK training. Like CESR/Portfolio Pathway, you’ll use evidence to back up your competencies and experience, but you will also use UK training to ensure you meet the requirements for getting on the specialist register. You might start training at ST3, ST4, or above to do this.
Getting GMC Registered with PLAB or MRCPCH
While MRCPCH and PLAB give you different starting points within the NHS, they both still hold the same weight when it comes to getting registered with the GMC. They prove – alongside other necessary evidence – that you are skilled enough and competent enough to work as a doctor in the UK. Here is what else you’ll need:
Proof of primary medical qualification
You’ll need to show evidence of your PMQ when applying for GMC registration.
Passport
You’ll also need your passport for your visa application and to travel to the UK in general.
Evidence of internship or other experience
The GMC requires at least one year of experience in a medical setting after attaining your PMQ.
Proof of your knowledge of English
To prove this, the GMC accepts both IELTS and OET. That won't be necessary if you attained your PMQ from an English-speaking country.
Certificate(s) of Good Standing
These certificates must come from any medical regulatory authority you’ve worked at in the last five years.
Fitness to practise
Within the GMC application, you’ll be asked questions to demonstrate your fitness to practise.
Your last five years of activity
Finally, you’ll need to showcase evidence of what you’ve been doing for the past five years – even if some of that time was spent out of work or education.
Luckily, it’s refreshingly simple to apply for GMC registration – you can do it all online and we’ve put together a comprehensive guide on How to Get GMC Registration for IMGs.
In Summary
The road to becoming a paediatrician in the UK is a lengthy and sometimes confusing one – especially when it comes to GMC registration and proving your knowledge/skills. In regards to PLAB vs. MRCPCH, here are the key points to keep in mind:
- MRCPCH offers a postgraduate qualification – PLAB is simply a common entryway to the UK.
- MRCPCH takes a longer time and costs more than PLAB.
- PLAB is only used for GMC registration.
- MRCPCH can get you into specialty training straight away.
- You can use MRCPCH to get CESR/Portfolio Pathway and get on the specialist register.
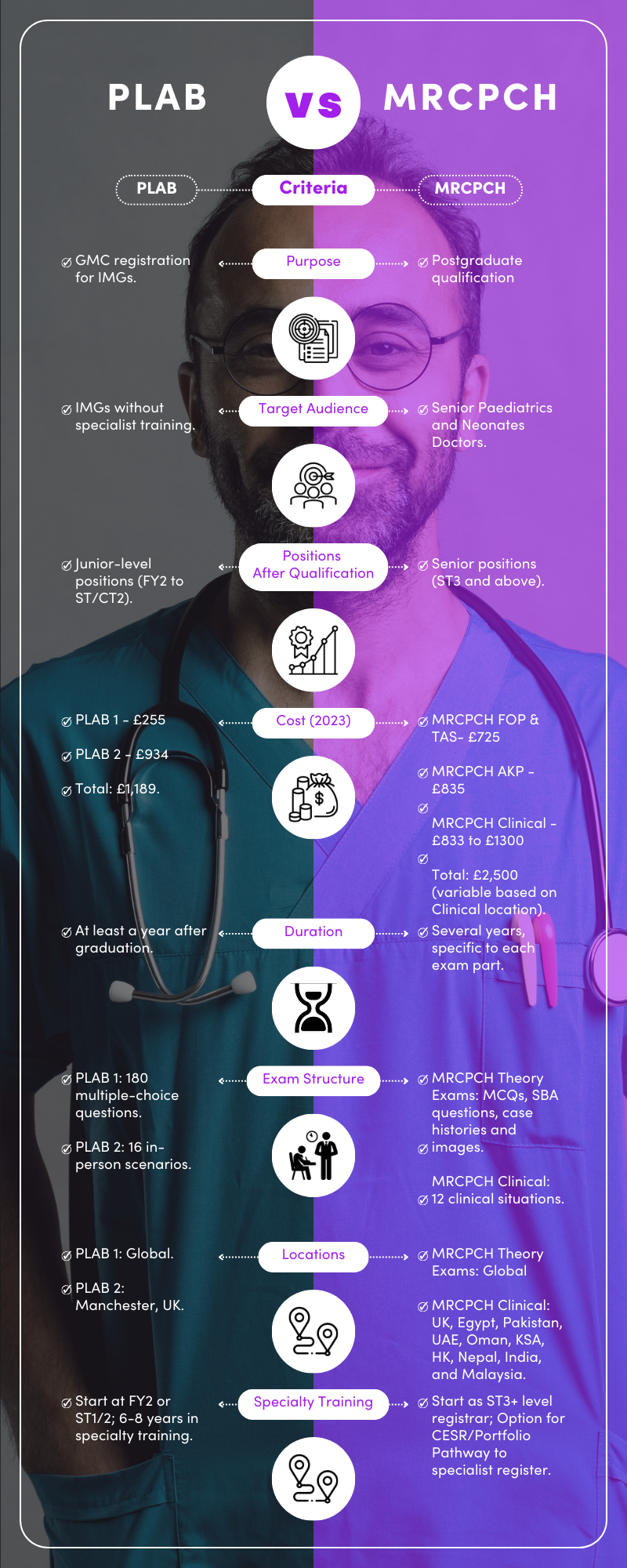
Using the above guide, you can determine which makes the most sense. The more research you do, the more you can be sure you’re taking the most appropriate route to GMC registration, ensuring that you start your UK medical career in a way that makes the most sense for your training and career goals.
Get in touch
If you’re an aspiring paediatrician or you’ve completed your training then reach out and let us help. BDI Resourcing have hundreds of 5-Star reviews from doctors around the world who we have helped to join more than 100 NHS Trusts. We would love for you to be the next success story.




